Identifying Parts of your Roof and Introduction to Common Roofing Terms
|
Hip Roof Features
Common features of hip roofs are defined in this section.
|
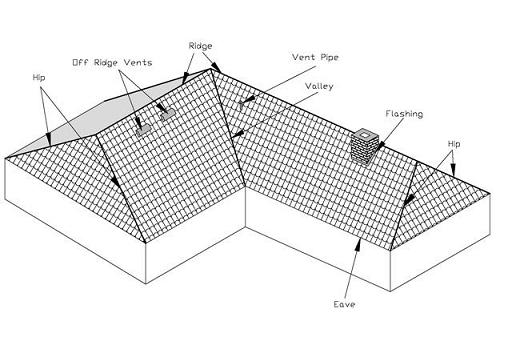
|
Common Features of Hip Roofs
(click image for larger version) |
Eaves - The lower roof edge from the wall of the house to
the outside of the fascia. Many roofers consider it to be the bottom
three feet of the roof.
Fascia - The vertical board or cover at the bottom edge of the
roof that encloses the ends of the rafters, trusses or extensions of
the rafters or trusses.
Flashing - Materials used to waterproof a roof along intersections
of walls, chimneys or dormers with the roof deck. Flashing is usually
pieces of metal or roll roofing used, around any intersection of roof
planes or projection of pipes or walls through the roof, to prevent water
leaks into a building. These projections may include vent pipes, chimneys,
adjoining walls, dormers and valleys.
Hip - The inclined external edge formed by the intersection of two
sloping roof planes. The hip runs from the ridge to the eaves.
Hip Roof - The end of a roof where three roof planes come together
to form two hips that run from a common ridge to the eaves.
Off-Ridge Vents - Attic ventilation provided through holes in the
roof, some distance off of the roof ridge, that are covered in such a way
that air can circulate through the attic but water intrusion is minimized,
at least for normal rain events.
Ridge - The uppermost horizontal edge of the roof that is formed by the
intersection of two sloping roof planes.
Valley - An area where two adjoining sloped roof planes intersect on a
roof and create an inside corner.
Vent Pipe - Typically these are pipes that vent the drainage system from
sinks, showers, bathtubs and toilets in your house. Where they pierce the roof
deck, they are usually sealed with a flange or boot that is sealed to the pipe
using flashing cement
|
Gable Roof Features
Common features of gable roofs are defined in this section.
|
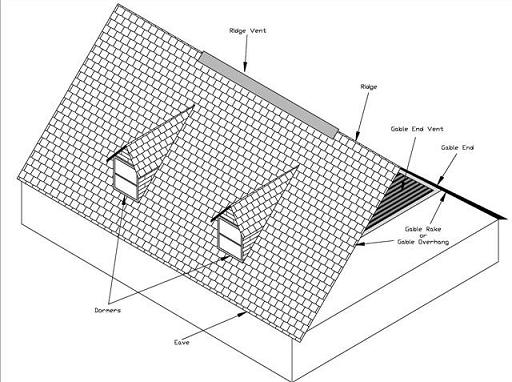
|
Common Features of Gable Roofs
(click image for larger version) |
Dormer - A raised roof, usually covering an area with a window and side
walls, extending out of a larger roof plane.
Gable End - The triangular portion of a sidewall that encloses the
end of a house beneath two sloping roof planes.
Gable End Vent - A vent in the gable end that allows natural ventilation
of the attic space.
Gable Rake - Sometimes called a gable overhang, this is the portion
of the roof that extends beyond the gable end. The gable rake is usually
supported by blocking and a fascia board that are attached to the last rafters
or truss (the gable rafters or gable truss) if the overhang is less than 12
inches or by an outrigger system if the overhang is greater than 12 inches.
Outriggers usually extend over the top of the last (gable) truss or rafters
and are anchored to the next set of rafters or truss in the roof system.
Ridge Vent - A vent that runs along the ridge of the roof. Usually
the roof deck is stopped short of the ridge to leave a gap for air ventilation
and this is covered by a plastic vent cover that is anchored to the roof deck
and allows air to escape from the top of the roof but minimizes the amount
of water that will be blown into the attic.
|
Other Terms
Other terms not shown in the sketches but extracted from Florida Roofing,
Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors Association, Inc. (FRSA) literature
at www.floridaroof.com are defined in
this section.
|
Asphalt - A bituminous waterproofing agent used in various types of
roofing materials.
Asphalt Concrete Primer - Asphalt based primer used to prepare concrete
and metal for asphalt sealant.
Asphalt Plastic Cement - Asphalt based sealant material, meeting ASTM
D4586 Type I or II. Used to seal and adhere roofing materials. Also called
mastic, blackjack, roof tar and bull.
ASTM - The American Society of Testing and Materials - a voluntary
organization that sets standards for a wide variety of materials, including
roofing.
Ballast - A material installed over the top of a roof membrane to help
hold it in place. Ballasts are loose laid and can consist of aggregate, or
concrete pavers.
Base Ply - The primary ply of roofing material in a roof system.
Base Sheet - An asphalt-impregnated, or coated felt used as the first
ply in some built-up and modified bitumen roof systems.
Blistering - Bubbles in roofing materials. Usually moisture related.
In shingles blisters are either moisture under the material or moisture
trapped inside the material.
Blow-offs - When shingles are subjected to high winds, and are forced
off a roof deck.
Buckling - When a wrinkle or ripple affects shingles or their underlayments.
Built-up Roofs (BUR) - A flat or low-sloped roof consisting of multiple
layers of asphalt and ply sheets.
Bundle - A package of shingles - there are 3, 4, and 5 bundles per square.
Butt Edge - The lower edge of the shingle tabs.
Cap Sheet - A granule-surfaced membrane often used as the top ply of
BUR or modified roof systems.
Caulk - To fill a joint with mastic or asphalt cement to prevent leaks.
Cement - See asphalt plastic cement.
Class "A" - The highest fire-resistance rating for roofing as per ASTM
E-108. Indicated roofing is able to withstand severe exposure to fire originating
from sources outside the building.
Class "B" - Fire-resistance rating that indicates roofing materials are able to withstand moderate exposure to fire originating from sources outside the building.
Class "C" - Fire-resistance rating that indicates roofing materials are able to withstand light exposure to fire originating from sources outside the building.
Coating - A layer of viscous asphalt applied to the base material into which granules or other surfacing is embedded.
Collar - Pre-formed flange placed over a vent pipe to seal the roof around the vent pipe opening - also called a vent sleeve.
Coping - The piece of material used to cover the top of a wall and protect it from the elements. It can be constructed from metal, masonry or stone.
Corrosion - When rust, rot or age negatively affect roofing metals.
Counter-Flashing - The metal or siding material that is installed over rooftop base flashing systems.
Course - A row of shingles or roll roofing running the length of the roof.
Coverage - Amount of weather protection provided by the roofing material. Depends on number of layers of material between the exposed surface of the roofing and the deck (i.e. - single coverage, double cover, etc.).
Crickets - A peaked water diverter installed behind chimneys and other large roof projections. Effectively diverts water around projections.
Cupping - When shingles are improperly installed over an existing roof or are over-exposed., they form a curl or cup.
Curb - A raised member used to support skylights, HVAC units, exhaust fans, hatches or other pieces of mechanical equipment above the level of the roof surface, and should be a minimum of eight inches in height.
Cutout - The open portions of a strip shingle between the tabs.
Deck - The substrate over which roofing is applied. Usually plywood, wood boards, or planks.
Downspout - A pipe for draining water from roof gutters - also called a leader.
Drip Edge - An installed lip that keeps shingles up off the deck at edges, and extends shingles out over eaves and gutters, and prevents water from backing up under shingles.
Dry-In - The process of installing the underlayment in the steep slope roofing making a low-slope roof watertight.
Eaves Flashing - Additional layer of roofing material applied at the eaves to help prevent damage from water backup.
End Laps - When installing rolled products in roofing, the area where a roll ends on a roof, and is overlapped by the next section of rolled material. (i.e. - underlayments, rolled roofing).
Exposure - The area on any roofing material that is left exposed to the elements.
Fasteners - Nails or staples used in securing roofing to the deck. Felt-organic or paper-based rolled material saturated with asphalt to serve as roofing underlayment.
Felt - Fibrous material saturated with asphalt and used as an underlayment or sheathing paper.
Fiberglass Mat - Fibers condensed into strong resilient mats for use in roof ing materials.
Field - Refers to the central part of a roof away from the perimeter.
Flange - Metal pan extending up and down a roof slope around flashing pieces. Usually at chimneys and plumbing vents.
Flashing Cement - Sealant designed for use around flashing ar4eas, typically thicker than plastic cement.
Gable Roof - Traditional roof style - two peaked roof planes meeting at a ridgeline of equal size.
Galvanize - To coat with zinc.
Granules - Crushed rock that is coated with a ceramic coating and fired, used as top surface on shingles.
Gutter - The trough that channels water from the eaves to the downspouts.
Hand-sealing - The method to assure sealing of shingles on every steep slopes, in high wind areas, when installing in cold weather.
Hand Lap - Shortest distance from the butt edge of an overlapping shingle to the upper edge of a shingle in the second course below. The triple coverage portion of the top lap of strip shingles.
Hip Legs - The down-slope ridges on hip roofs.
Laminated Shingles - Shingles made from two separate pieces that are laminated together - also called dimensional or architectural shingles.
Laps - The area where roll roofing or rolled underlayments overlap one another during application (also see side laps and end laps).
Lap Cement - An asphalt-based cement used to adhere overlapping piles of roll roofing.
Low Slopes - Roof pitches less than 4/12 are considered low sloped roofs. Special installation practices must be used on roofs sloped 2/12-4/12.
Masonry Primer - An asphalt-based primer used to prepare masonry surfaces for bonding with other asphalt products.
Mastic - See asphalt plastic cement.
Mats - The general term for the base material of shingles and certain rolled products.
Membrane - The portion of the roofing system that serves as the waterproofing material. Can be composed of one material or several materials laminated together.
Mineral-surfaced Roofing - Asphalt shingles and roll roofing that are covered with granules.
Modified Bitumen - Rolled roofing membrane with polymer modified asphalt and either polyester or fiberglass reinforcement.
Mopping - To apply hot asphalt or coat tar using a hand mop or mechanical applicator.
Nail Guide Line - Painted line on laminated shingles, to aid in the proper placement of fasteners.
Nail Pop - When a nail is not fully driven or backs out of the deck, it sits up off the roof deck.
Open Valley - Valley installation using metal down the valley center
Organic Mat (Felt) - Materials made from recycled wood pulp and paper
Organic Shingles - Shingles made from organic (paper) mats.
Over Driven - The term used for fasteners driven through roofing material with too much force, breaking the material.
Over Exposed - Installing shingle course higher than their intended exposure.
Overhang - That portion of the roof structure that extends beyond the exterior walls of a building.
Penetration - Any object that pierces the surface of the roof.
Pitch - Ration of the rise of the roof, in inches, to the span of the roof, in feet (i.e. -4/12)
Power Vents - Electrically powered fans used to move air from attics and structures.
Plastic Cement - Asphalt based sealant, also called bull, mastic, tar and asphalt cement.
Plumbing Vents - Terms used to describe plumbing pipes that project through a roof plane, also called vent stacks.
Ply - The number of layers of roofing (i.e. - one-ply, two-ply).
Ponding - The accumulation of water at low-lying areas on a roof.
Quick-setting Cement - An asphalt-based cement used to adhere tabs of strip shingles to the course below. Also used to adhere roll roofing laps applied by the concealed nail method.
Racking - Roofing application method in which shingle courses are applied vertically up the roof rather than across an dup. Not a recommended procedure.
Rafter - The supporting framing member immediately beneath the deck, sloping from the ridge to the wall plate.
Release Tape - A plastic or paper strip that is applied to the back of self-sealing shingles. This strip prevents the shingles from sticking together in the bundles, and need not be removed for application.
Roll Roofing - Asphalt roofing products manufactured in roll form.
Roofing Tape - An asphalt-saturated tape used with asphalt cements for flashing and patching asphalt roofing.
Saturated Felt - An asphalt-impregnated felt used as an underlayment between the deck and the roofing material
Self-sealant - Sealant installed on shingles. After installation, heat, and sun will activate sealant to seal the shingles to each other.
Self-sealing Shingles - Shingles containing factory-applied strips or spots for self-sealing adhesive.
Self-sealing Strip or Spot - Factory-applied adhesive that bonds shingle courses together when exposed to the heat of the sun.
Side Laps - The area on rolled material where one roll overlaps the rolled material beneath it. Also called the selvage edge on rolled roofing.
Side Walls - Where a vertical roof plane meet a vertical wall - the sides or dormers, etc.
Soffit Ventilation -Intake ventilation installed under the eaves, or at the roof edge.
Soil Stack - A vent pipe that penetrates the roof.
Square - A unit of roof measure covering 100 square feet.
Square-tab Shingles - Shingles on which tabs are all the same size and exposure.
Starter Strip - The first course of roofing installed, usually trimmed from main roof material.
Steep Slope Roofing - Generally all slopes higher than 4/12 are considered steep slopes. A method of installing asphalt shingles on roof slopes greater than 21 inches per foot.
Strip Shingles - Asphalt shingles that are approximately three times as long as they are wide.
Tab - The bottom portion of traditional shingle separated by the shingle cutouts.
Tear-offs - Removal of existing roofing materials down to the roof deck.
Three-dimensional Shingles - See laminated shingles.
Three-tab Shingles - The most popular type of asphalt shingle usually 12"x36" in size with three tabs.
Top Lap - That portion of the roofing covered by the succeeding course after installation.
UL - Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
UL Label - Label displayed on packaging to indicate the level of fire and/or wind resistance of asphalt roofing.
Underlayments - Asphalt based rolled materials, which are designed to be installed under main roofing material, to serve as added protection.
Vapor Retarder - Any material used to prevent the passage of water vapor.
Vent - Any outlet for air that protrudes through the roof deck such as a pipe or stack. Any device installed on the roof, gable or soffit for the purpose of ventilating the underside of the roof deck.
Ventilation - The term used in roofing for the passage of air from an enclosed space.
Warranty - The written promise to the owner of roofing materials for material related problems.
Waterproof Underlayments - Modifies bitumen based roofing underlayments, which are designed to seal wood decks and waterproof critical leak areas.
Weep Holes - Small holes used to permit moisture to drain that has gathered inside a building component.
Wind Clip - A clip that slips over the ends of tile, slate and other steep slope roofing material sin order to help prevent wind uplift damage.
Wind Load - The force that wind puts on structures.
Wind Uplift - The upward displacement of a section of a roof system or component caused by movement of air from a location of higher air pressure, to an area of lower air pressure. Strong wind along the surface of a roof, especially at comers and along perimeters, creates low air pressure above the surface of the roof. Displacement or blow-off of shingles or other roofing caused by the wind.
Back to main roofing page
|

